Albert Reynolds
Program in Cancer Biology
Epithelial Biology Center (EBC)
Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center (VICC)
The Reynolds laboratory combines molecular and biochemical approaches with 3D (organoid) culture and mouse models of colon and breast cancer to examine roles of p120-catenin (p120) in cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion, tumorigenesis and metastasis. A recent focus involves p120 signaling to the nucleus through Kaiso (aka ZBTB33), a p120-associated transcription factor involved in genetic and epigenetic regulation of stem-cell function and tissue differentiation. The lab is interested in defining the nuclear functions of Kaiso and p120 using state of the art next generation sequencing technologies, including ChIPseq, PROseq and ATACseq.
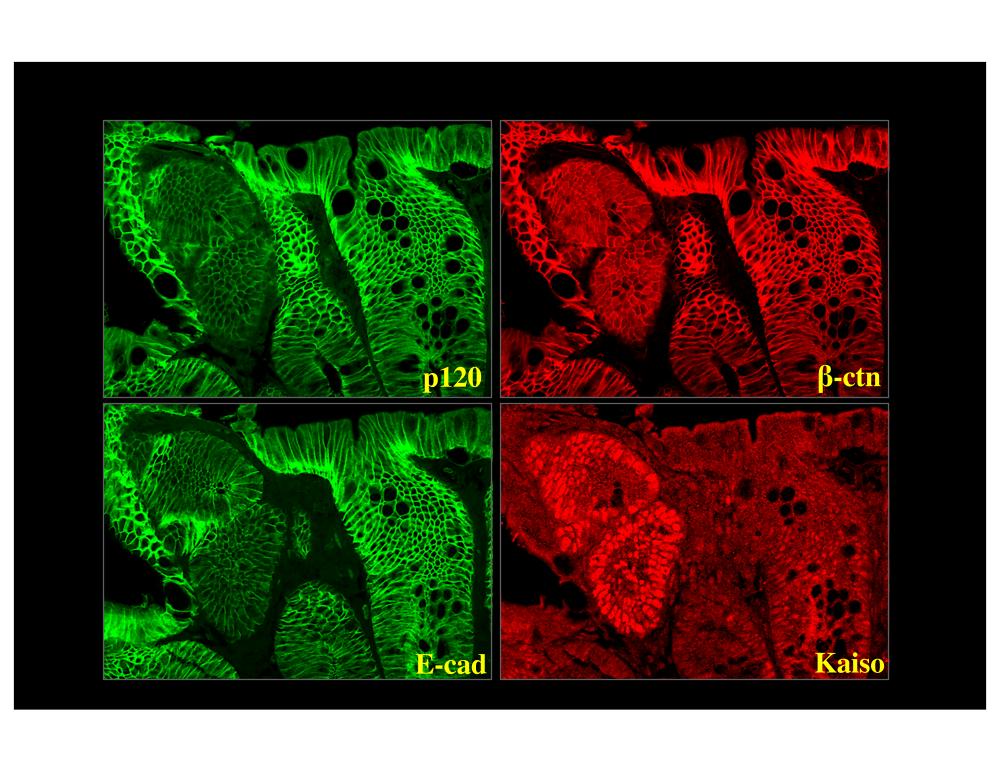
The Reynolds laboratory combines molecular and biochemical approaches with 3D (organoid) culture and mouse models of colon and breast cancer to examine roles of p120-catenin (p120) in cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion, tumorigenesis and metastasis. A recent focus involves p120 signaling to the nucleus through Kaiso (aka ZBTB33), a p120-associated transcription factor involved in genetic and epigenetic regulation of stem-cell function and tissue differentiation. The lab is interested in defining the nuclear functions of Kaiso and p120 using state of the art next generation sequencing technologies, including ChIPseq, PROseq and ATACseq.
Keywords: p120-catenin , E-cadherin , Kaiso , stem cells , mouse models of cancer , metastasis
Research Area: Stem Cell Biology & Regeneration , Epithelial Biology , Gene Regulation , Cancer Biology , Molecular Pathology