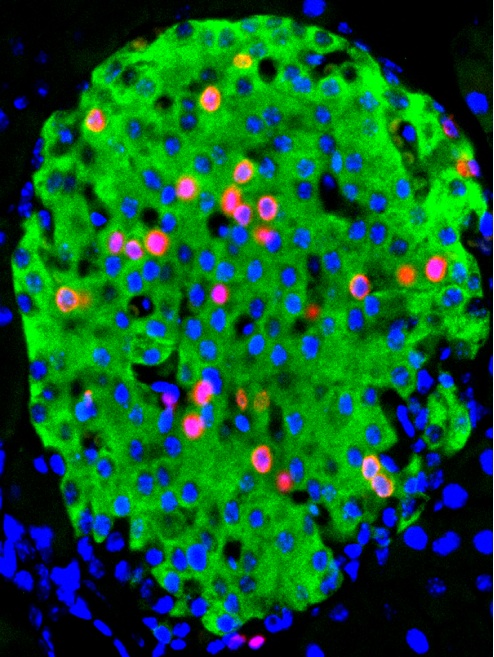
Loss of Foxd3 results in decreased beta cell proliferation and glucose intolerance during pregnancy
Jennifer L. Plank, Audrey Y. Frist, Alison W. LeGrone, Mark A. Magnuson and Patricia A. Labosky
– Author Affiliations
Department of Cell and Developmental Biology (J.L.P., A.Y.F., A.W.L., M.A.M., P.A.L.), Center for Stem Cell Biology (J.L.P., A.Y.F., A.W.L., M.A.M., P.A.L.), Program in Developmental Biology (J.L.P., A.Y.F., A.W.L., M.A.M., P.A.L.), Department of Molecular Physiology and Biophysics (M.A.M.), and Department of Pharmacology (P.A.L.), Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee 37232-0494
Address all correspondence and requests for reprints to: Patricia A. Labosky, 9415D MRBIV, 2213 Garland Avenue, Nashville, Tennessee 37232-0494. E-mail: trish.labosky@vanderbilt.edu.
Abstract
A complete molecular understanding of β-cell mass expansion will be useful for the improvement of therapies to treat diabetic patients. During normal periods of metabolic challenges, such as pregnancy, β-cells proliferate, or self-renew, to meet the new physiological demands. The transcription factor Forkhead box D3 (Foxd3) is required for maintenance and self-renewal of several diverse progenitor cell lineages, and Foxd3 is expressed in the pancreatic primordium beginning at 10.5 d postcoitum, becoming localized predominantly to β-cells after birth. Here, we show that mice carrying a pancreas-specific deletion of Foxd3 have impaired glucose tolerance, decreased β-cell mass, decreased β-cell proliferation, and decreased β-cell size during pregnancy. In addition, several genes known to regulate proliferation, Foxm1, Skp2, Ezh2, Akt2, and Cdkn1a, are misregulated in islets isolated from these Foxd3 mutant mice. Together, these data place Foxd3 upstream of several pathways critical for β-cell mass expansion in vivo.